Chapter 2: AI vs. ML vs. DL#
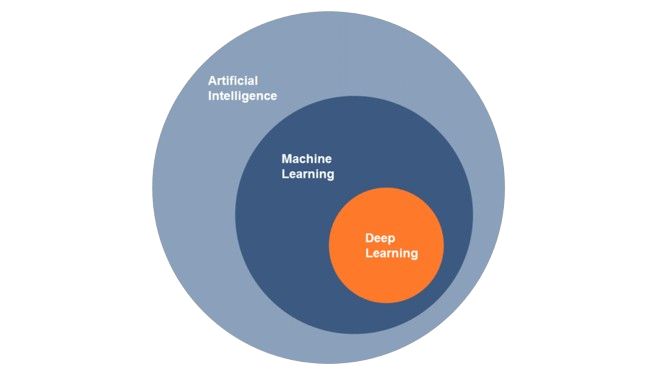
Artificial Intelligence (AI): A broad field focused on creating systems that can perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding language. AI aims for general cognitive abilities, often mimicking human decision-making.
Example: Chatbots, autonomous vehicles, recommendation systems.Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI, where algorithms learn from data to improve performance on a specific task without being explicitly programmed. It focuses on pattern recognition and prediction through supervised, unsupervised, or reinforcement learning.
Example: Spam detection, customer segmentation, and predictive maintenance.Deep Learning (DL): A subset of ML using neural networks with multiple layers (deep neural networks). It excels in processing large datasets and complex data like images, audio, and text, making it suitable for tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving.
Example: Image recognition, voice assistants, and language translation.
The hierarchy is: AI > ML > DL, where each represents a more specialized approach to building intelligent systems.
